June 22, 2023 by EMPWellness Admin
Cholesterol in normal levels is an essential substance for the body. However, if the blood concentration becomes too high, it becomes a silent danger that puts people at risk of heart attack. Cholesterol is present in all cells of the body and has important natural functions in food digestion, hormone production and vitamin D production. The body produces it, but people also consume it in food. Cholesterol is waxy and fat-like in appearance.
There are two types of cholesterol:
- Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) or “bad” cholesterol.
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL) or “good” cholesterol.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is an oil-based substance and does not mix with blood, which is water-based. This substance moves throughout the body along with lipoproteins.
Two types of lipoproteins carry cholesterol packages:
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL): Cholesterol that moves this way is unhealthy or “bad” cholesterol.
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL): The cholesterol found in HDL is known as “good” cholesterol.
Cholesterol has four main functions without which we cannot survive. Functions such as the following:
- Contribute to the structure of cell walls
- Formation of digestive bile acids in the intestine
- It allows the body to produce vitamin D.
- It enables the body to produce certain hormones.
Causes of high cholesterol
High cholesterol is an important risk factor for coronary heart disease and heart attack.
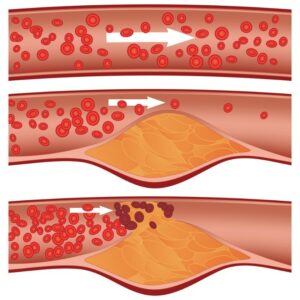
Cholesterol build-up is part of a process that narrows the arteries, called atherosclerosis. In this situation, in atherosclerosis, plaque is formed and restricts blood flow.
Reducing dietary fat intake helps manage cholesterol levels. In particular, limit foods that contain the following ingredients:
Cholesterol: This type of cholesterol is found in animal foods, meat and cheese.
Saturated fat: This compound is found in some meats, dairy products, chocolate, baked goods, fried and processed foods.
Trans fats: This substance is found in some fried and processed foods.
Being overweight or obese can also lead to an increase in blood LDL levels. Genetic factors can also play a role in increasing cholesterol. People with hereditary familial hypercholesterolemia have very high LDL levels.
Other conditions that can lead to high cholesterol levels include:
- diabetes
- Liver or kidney disease
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Pregnancy and other conditions that increase the level of female hormones
- Underactive thyroid gland
Medicines that raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol, such as progestins, anabolic steroids, and corticosteroids
Symptoms of high cholesterol
A person with high cholesterol levels often has no signs or symptoms, but screening and regular blood tests can help detect high levels. A person who doesn’t get tested can have attacks and conditions like congestive heart failure without warning because they don’t know they have high cholesterol levels. Regular tests can help reduce this risk.
Cholesterol in foods
A Harvard report has identified 11 cholesterol-lowering foods that actively lower cholesterol levels. These foods include the following:
- Oat
- Oats and whole grains
- Beans
- Eggplant and okra
- nuts
- vegetable oil (canola, sunflower)
- Fruits (apples, grapes, strawberries and citrus fruits)
- Soy and soy-based foods
- Fatty fish (especially salmon, tuna, and sardines)
- Foods rich in fiber
Adding these foods to a balanced diet can help control cholesterol.
In the same report, a list of harmful foods for cholesterol levels is also mentioned. These foods include the following:
- Red Meat
- Full fat dairy products
- Margarine
- Hydrogenated oils
- Semi-finished products with preservatives
- Prevent high cholesterol
People who want to lower or maintain cholesterol levels can make four important lifestyle decisions:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet.
- exercise regularly.
- Avoid smoking.
- Reach a balanced weight and maintain it.
- These measures reduce the risk of coronary heart disease and heart attack.
Since 2013, guidelines for reducing or preventing high cholesterol have focused on addressing the risks of an unhealthy lifestyle, even at an early age.
When you see your doctor, you’ll likely be asked questions about the following factors that may increase your risk:
- Family history and ethnicity
- Certain health conditions that increase the risk of high cholesterol, such as chronic kidney disease or chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Considering these factors leads to a more personalized approach to treating and preventing high cholesterol levels.
How can high cholesterol be treated?
There are different ways to treat high cholesterol. These methods include the following:
Fat reduction treatment
For people with high cholesterol levels, drug treatment depends on cholesterol levels and other risk factors. Treatment usually starts with diet and exercise, but people at high risk of heart attack may need statins or other drugs.
Statins are the main group of cholesterol-lowering drugs. In addition to statins, your doctor may prescribe the following:
- Selective cholesterol absorption inhibitors
- Resins
- Fibrates
- niacin
In 2017, researchers noted that a new drug, called ezetimibe, could significantly reduce the risk of a major cardiovascular event in people at high risk of such events. Etezimibe lowers fat levels by limiting the absorption of cholesterol in the gut.
If a person has already had a cardiovascular event, such as a heart attack, the doctor may recommend using ezetimibe as well as a statin.
- Statin safety
- The use of statins, like all drugs, can have side effects.
These complications include the following:
Statin-induced myopathy (a disease of muscle tissue)
tiredness
The risk of diabetes (diabetes symptoms may be more severe in these people)
A person should not stop taking statins without consulting a doctor, as it may increase the risk of cardiovascular problems.
If you see side effects, your doctor may suggest the following:
Change to another drug
Increasing efforts to lower cholesterol through lifestyle changes
Complications of high cholesterol
Cholesterol levels play an important role in heart attack risk over the next 10 years.
Factors affecting this situation include the following:
- Age
- Sex
- Cholesterol level
- Smoking status
- blood pressure
These factors are a set of stimuli to increase the risk of heart attack, most of which can be controlled by following a healthy lifestyle. If you feel any symptoms, go to your doctor to find out about your cholesterol level in order to be sure by doing the necessary tests. It is better to know that high cholesterol, like many other diseases, is easier to control with early detection.
Thank you
